What is Die Casting Molds and How Do They Work?
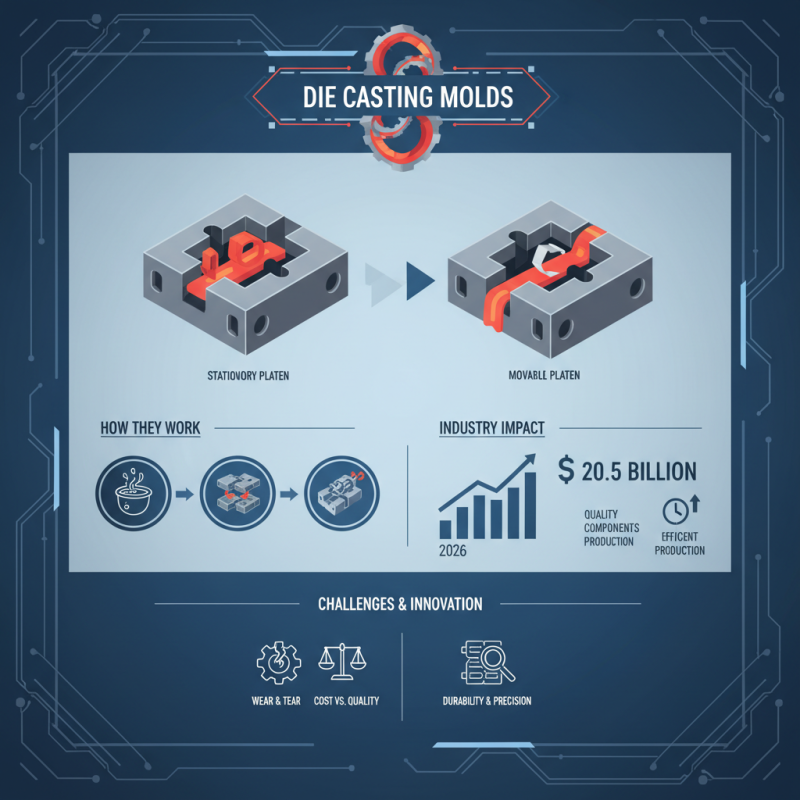
Die Casting Molds play a crucial role in the manufacturing industry. These molds are essential for creating precise and complex metal parts. According to a recent market report by Mordor Intelligence, the global die casting market is expected to reach $20.5 billion by 2026. This growth highlights the increasing demand for high-quality components in various industries.
Expert Robert Anderson, a veteran in the die casting field, states, "Die casting molds are not just tools; they are the backbone of efficient production." His insights emphasize the significance of these molds in enhancing operational efficiency and productivity. However, there is still room for improvement in mold design and material use. Many manufacturers struggle with achieving the ideal balance between cost-efficiency and quality.
Issues like wear and tear can lead to production delays and increased costs. In this fast-paced industry, it’s vital for companies to continually innovate their die casting processes. Focusing on durability and precision will make all the difference. Hence, understanding die casting molds' functionality is more important than ever in today’s competitive landscape.
What are Die Casting Molds?
Die casting molds are essential tools in the manufacturing process. They are used to create metal parts with high precision. Typically made of steel or aluminum, these molds can withstand high-pressure conditions. It’s fascinating to see how molten metal is injected into molds. This method allows for complex shapes and detailed designs.
The die casting process involves both creative and technical challenges. Achieving the right temperature for the molten metal is crucial. Even a slight deviation can lead to defects. The cooling phase is equally important. If the metal cools too slowly, warping may occur. These challenges highlight the need for careful monitoring.
While die casting molds can produce high-quality products, imperfections can happen. For example, trapped air can create bubbles in the final product. These flaws can impact the overall integrity of the piece. Manufacturers often spend time refining their techniques to minimize issues. Embracing these challenges can lead to improved designs and better outcomes.
The Materials Used in Die Casting Molds
Die casting molds play a crucial role in producing high-quality metal parts. The material selection for these molds significantly affects their performance and lifespan. Most die casting molds are made from steel or aluminum, chosen for their durability and thermal properties. Steel molds, particularly those made from tool steel, are ideal for high-volume production. They can withstand the heat generated during the casting process. Using steels like H13 can provide a longevity of up to 1 million cycles.
Aluminum molds are another option, often favored for their lighter weight and lower cost. However, they may not last as long as steel molds. Reports indicate that aluminum molds can typically achieve around 100,000 cycles. This lower durability can impact manufacturing efficiency and cost over time.
In addition to steel and aluminum, some molds incorporate specialty materials. These materials might enhance thermal conductivity or reduce wear. The choice of material directly influences the casting's surface finish and dimensional accuracy. Industry data shows that optimizing material selection can reduce scrap rates by 20%. Nevertheless, finding the right balance between cost and performance often remains a challenge for manufacturers.
The Die Casting Process Explained
The die casting process is a fascinating method used to create metallic parts. It begins with molten metal, which is forced into a mold cavity under pressure. This technique is efficient for producing complex shapes that require tight tolerances. It can manufacture numerous pieces quickly, which is great for large-scale production. The molds used are often made from high-strength materials, which ensures they can withstand multiple cycles.
However, not everything goes smoothly. Sometimes the molds can wear out, leading to defects in produced parts. Porosity is another common issue; bubbles can form in the metal as it's cast. This can compromise the strength of the final product. Proper maintenance and periodic inspections of the molds are essential but often overlooked. The process also requires skilled operators to monitor variables like temperature and pressure, which can vary.
In the end, while die casting is an excellent method for producing metal components, it is not perfect. Understanding its intricacies can help improve quality and efficiency. It’s important to regularly evaluate both the molds and the process. Refinement and learning from failures are key to achieving better results in die casting.
Maintenance and Care for Die Casting Molds
Die casting molds require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance. Proper care can extend their lifespan significantly. According to industry data, well-maintained molds can last up to 3 times longer than neglected ones. Regular inspections should focus on wear and tear, especially around ejector pins and cavity surfaces. Keeping the molds clean from debris is critical. A simple cleaning routine can prevent costly repairs.
Lubrication also plays a vital role in maintaining die casting molds. Using high-quality lubricants helps reduce friction and heat build-up during casting. Inadequate lubrication can lead to mold damage and product defects. It's essential to analyze lubrication patterns regularly and adjust them as needed.
Despite these best practices, issues can still arise. Overheating is a common problem in die casting. Continuous monitoring of temperatures can prevent this issue. Identifying any signs of wear early can save time and resources in the long run. There’s always room for improvement. Each experience teaches valuable lessons about processes and maintenance best practices.
Applications of Die Casting in Various Industries
Die casting plays a vital role in multiple industries, contributing to efficiency and precision. It is a manufacturing process where molten metal is forced into molds. The automotive industry, for instance, heavily relies on die casting. According to market analysis, around 80% of vehicle components can be produced using this method. This includes engine blocks and transmission cases.
Electronics also leverage die casting. Manufacturers use it for enclosures and heat sinks. Research indicates that the electronics sector will grow by 5.6% annually. This growth drives more demand for high-quality die casting parts. Yet, challenges remain. Some manufacturers struggle with defects in the casting process. Achieving the ideal balance between pressure and temperature is critical. Small variations can lead to significant quality issues.
Aerospace is another sector benefiting from die casting. It ensures lightweight and strong components essential for performance. Reports suggest that lightweight materials can reduce fuel consumption by 20%. Despite this, the industry faces pressure to meet strict regulatory standards. As technology evolves, refining die casting techniques is crucial for maintaining competitiveness.
What is Die Casting Molds and How Do They Work? - Applications of Die Casting in Various Industries
| Industry | Common Applications | Materials Used | Advantages of Die Casting |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Engine components, transmission cases | Aluminum, zinc alloys | High precision, excellent surface finish |
| Aerospace | Structural components, brackets | Magnesium, aluminum | Lightweight, durable |
| Consumer Electronics | Housing, frames | Zinc, aluminum | Complex shapes, smooth finishes |
| Industrial Machinery | Pumps, valves, housings | Aluminum, magnesium | High efficiency, cost-effective |
| Construction | Fasteners, brackets | Zinc, aluminum alloys | Strength, corrosion resistance |